299 million years B.C to 140 million years B.C
299 million years B.C
Permian Era
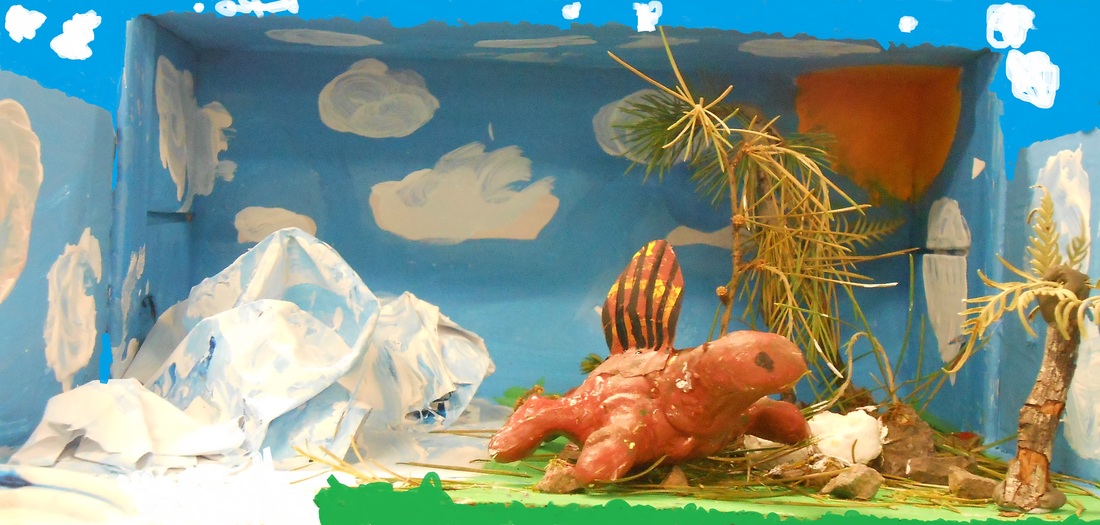
In the Permian Era (299-251 million years B.C) Australia was connected to a huge continent called Pangea. The northern part of Australia was desert but the southern part was ice. Victoria was covered in a slow moving ice sheet. When the ice melted and retreated seed ferns, tree ferns, horse tails and club mosses grew. When the land became drier, conifers, cycads and ginkgos grew. On land, where there were plants, animals lived. There were lots of fish and invertebrates in the sea. The ancestors of animals we see today survived in small groups. Reptiles such as Dimetrodon were early dinosaurs. Near the end of the Permian Era, there was a mass extinction. The extinction killed 90% of the earth’s species. There was no food for large plant eating reptiles and there was no habitat for insects.
Permian Era
In the Permian Era (299-251 million years B.C) Australia was connected to a huge continent called Pangea. The northern part of Australia was desert but the southern part was ice. Victoria was covered in a slow moving ice sheet. When the ice melted and retreated seed ferns, tree ferns, horse tails and club mosses grew. When the land became drier, conifers, cycads and ginkgos grew. On land, where there were plants, animals lived. There were lots of fish and invertebrates in the sea. The ancestors of animals we see today survived in small groups. Reptiles such as Dimetrodon were early dinosaurs. Near the end of the Permian Era, there was a mass extinction. The extinction killed 90% of the earth’s species. There was no food for large plant eating reptiles and there was no habitat for insects.
|
251-199 million years B.C
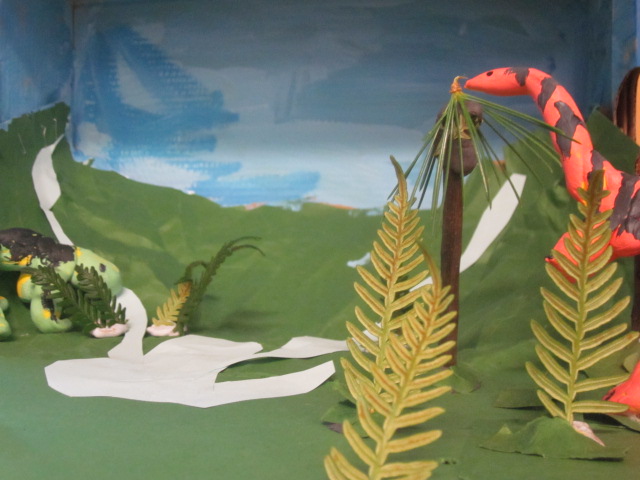
Triassic period At the end of the Permian period there was a mass extinction and it destroyed most living things. Therefore, it took a long time for different plant and animal species to evolve during the Triassic Era. The remaining sea life was slow to evolve new species because of things like low oxygen after the extinction. Cladiscities, a surviving cephalopod, was about 17cm long. Many corals died but the modern scleractinian corals evolved later in the Triassic. There were no polar ice caps. The valleys that were created by ice glaciers were green with conifers and ferns now that it was warmer. Some of the plants and animals that lived were the Lystrosaurus (an early herbivore that may have been an ancestor of mammals and reptiles), the Clatrotitan (an insect that looks like a praying mantas crossed with a dragonfly and its wing span was approximately 30cm), the Thinnfeldia (a fern that was common back in the Triassic period) and Coelophysis (an early dinosaur that was about 3 metres long and was a carnivore). |
|
199 million years B.C
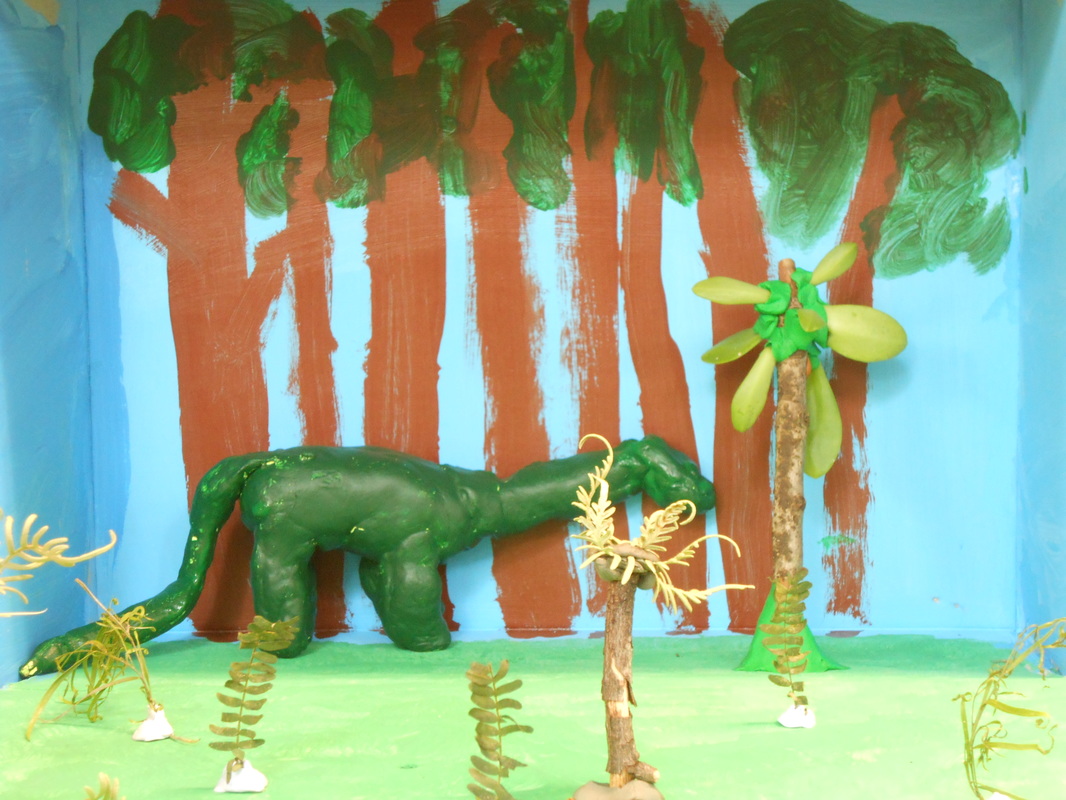
Jurassic Era In the Jurassic period, the first mammals evolved and plants developed defenses against dinosaurs. Dinosaurs grew tall, but plants grew taller; sometimes up to 90 metres tall! Plants also developed wood to help them grow so tall. Also plants developed spiky leaves or poisons to stop the dinosaurs from eating them. Plants evolved to communicate when things were coming to eat them. They use gases. Plants were mostly ferns and conifers. The Earth’s crust was moving and Australia was breaking apart from Antarctica. The climate was warmer even though it was close to Antarctica. |
|
140 million years B.C
The First Flower. The first flowering plant came 140 million years B.C and, having seeds, allowed plants to grow in places where there was no water for some of the year. Seeds waited until the rain came before they started to grow. Now there are lots more plants growing on the Earth! |
145 million years B.C
Cretaceous Period At the start of the Cretaceous period, the world was warm and had no polar ice caps. The largest animals were reptiles like dinosaurs, flying pterosaurs, dolphin-like ichthyosaurs and giant sea turtles. The only mammals on earth were very small and flowering plants started to evolve and spread across the world. All this changed 65.5 million years ago at the end of the Cretaceous Era. As you might know this was the extinction of the dinosaurs, sea reptiles, flying reptile’s and sea invertebrates. The most likely culprit was a huge asteroid called Ejector. It projected huge clouds of dust into the sky which blocked out the sunlight killing the plants and affecting food chains. Victoria was close to the south pole and one of the coolest places on the planet at the time. Victoria and Antarctica were covered in temperate forests of conifers and ferns. Life was very hard for the dinosaurs that lived there, because of long periods with no sunlight. Australia was separate from Gondwana with lots of rift valleys with streams, forest and volcanoes in them. In the streams species of fish, aquatic reptiles, and ferocious amphibious tetrapods such as Koolasuchus evolved. |